However, if the annuitant happens to live longer than the registered life expectancy, there is a possibility they receive more than the accumulated value of their annuity. The annuitization phase is more of a single, immediate event rather than a phase, acting as a separation between the accumulation and payout phases. The decision to annuitize is final, and once made, it is not possible to request a different form of payout or access the principal. You can access your pension funds from age 55 and you don’t need to retire to do so.
Calculating the Future Value of an Annuity Due
You may also receive more income by choosing to be paid annually rather than monthly. There is no limit on the number of pensions you can have so there is no limit on the number of annuities you can have. You can use each pension fund to buy a separate annuity, so you have as many annuities as you do pension funds. This is provided they are over the value of £2,000, before any tax-free cash has been taken. Having more than one annuity allows you to choose different options for each annuity. You don’t have to buy your lifetime annuity from your current pension provider.
Are annuities a good investment?
Directly sold products, which you buy straight from the insurer, can help you get around that big upfront fee. Fixed annuities are for the people who look for security the most; however, they will most likely lose buying power because of inflation. In contrast, variable annuities can return much more but have the value fluctuation characteristic. This approach may sound straightforward, but the computation may become burdensome if the annuity covers an extended interval.
The Annuity Formula for the Present and Future Value of Annuities
This makes it financially undesirable from a tax minimization standpoint. There are several options for choosing how annuity payouts occur, and not all annuities offer every payout option. The Annuity Payout Calculator only calculates fixed payment or fixed length, two of the most common options. Annuity in arrears—a legal, accounting and actuarial term—is also known as an „ordinary annuity.“ The opposite of an annuity in arrears is known as an „annuity in advance“ or „annuity due.“ Annuity in arrears refers to the payment of an equal amount of money that is made at the end of a regular term. It does not refer to an annuity product, per se, but instead refers to a payment structure that an annuity might employ.
„You’re not going to run out of money but it can continue to go lower if the market continues to go lower,“ said Evan Potash, an executive wealth management advisor at TIAA. „If you look at markets over the long term, though, they tend to go up much more than they go down.“ Only 36% of Americans saving for retirement expect to have enough to be financially secure when they retire, according to an AARP survey from January 2024. The biggest risk with most retirement planning is outliving your savings. In Excel, the PV and FV functions take on optional fifth argument which selects from annuity-immediate or annuity-due. 1035 Exchanges (including partial 1035 exchanges) involve a complex set of tax rules and regulations.
Find the investment option that works for you
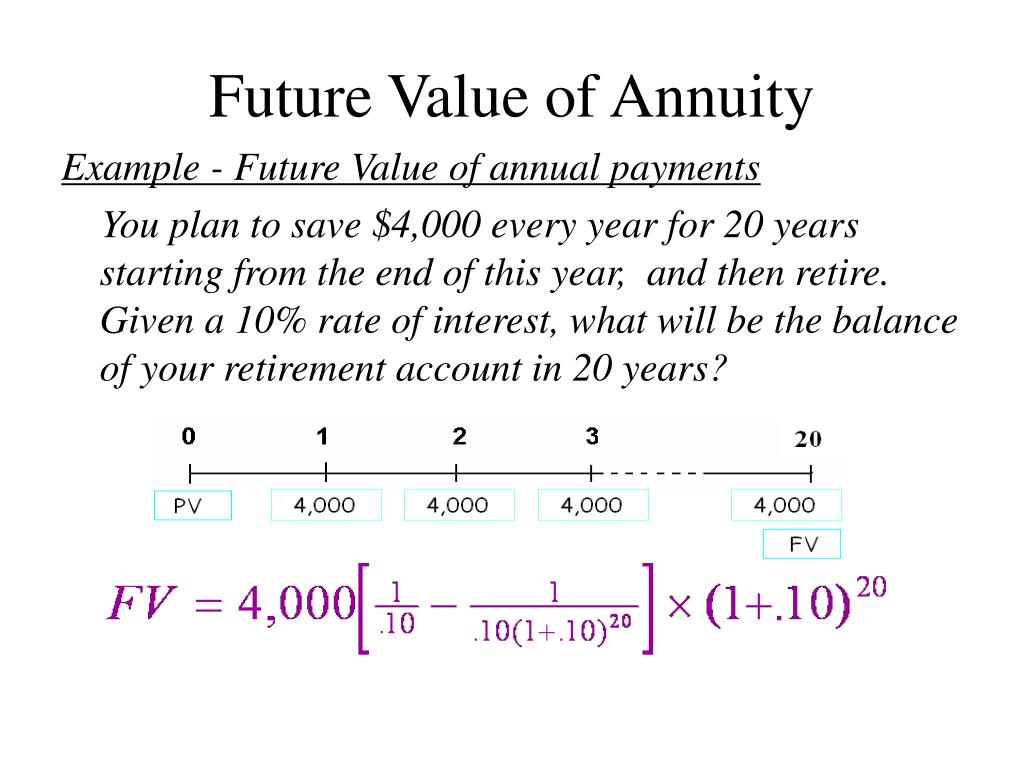
To account for payments occurring at the beginning of each period, the ordinary annuity FV formula above requires a slight modification. In contrast to the FV calculation, PV calculation tells you how much money would be required now to produce a series of payments in the future, again assuming a set interest rate. In order to qualify, distributions must not be taken from either contract within 180 days of the exchange. While partial exchanges are allowed by the IRS, many insurance companies do not provide this service. Most annuity contracts allow the withdrawal of a portion of the account value each year without incurring a surrender charge.
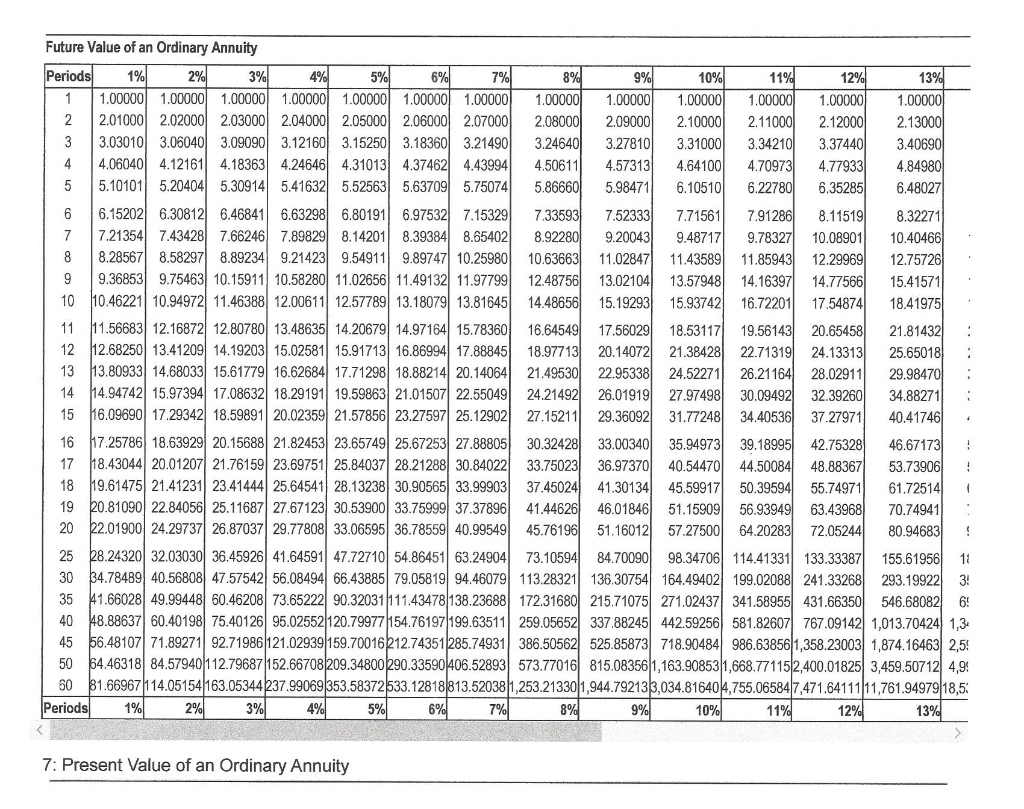
The payments (deposits) may be made weekly, monthly, quarterly, yearly, or at any other regular interval of time. Annuities may be calculated by mathematical functions known as „annuity functions“. This option combines features of the fixed length and life-only options. If the annuitant dies after the period certain, no payments are made to the beneficiary. You can choose to have your income increase annually, to keep up with inflation.
- If you have a standard single lifetime annuity, with no added options, when you die your income payments will stop.
- This section defines the characteristics of four different types of payment series and then contrasts them to the Chapter 9 and Chapter 10 single payment calculations.
- An Annuity is a type of bond that offers a stream of periodic interest payments to the holder until the date of maturity.
Each timeline in these figures assumes a transaction involving six semi-annual payments over a three-year time period. Before you get to that date, your money has the opportunity to either accrue interest (fixed annuities) or benefit from market gains (variable annuities). The present value of the ordinary annuity formula considers the dollar amount of each payment, the discount rate, and the number of payments. The present value of the annuity due formula uses the same inputs but adjusts for the earlier payment timing. A fixed annuity has a flat rate of return, regardless of what happens with the market or inflation. Fixed annuities offer peace of mind and few or no fees, though they usually don’t pay out as much as variable accounts.
The discount rate reflects the time value of money, while the interest rate applied to the annuity payments reflects the cost of borrowing or the return earned on the investment. Reflexively, if you are the party receiving a payment, an annuity due (or annuity in advance) is preferable for the same reason. If you die in the early years of your annuity plan, the total income you receive may be less than the pension fund used to buy the annuity. Selecting a death benefit, either value protection or a guarantee period, allows you some protection against this.
This option ensures that retirement income provided by an annuity will continue for a spouse in the case of the death of the main annuitant. Payments are calculated annuity in advance and based on the life expectancy of the main annuitant and their spouse. Due to this, payments under this option will generally be lower than the life-only option.
Besides, you can find the annuity formulas and get some insight into their mathematical background. Depending on the type of annuity you buy, your annuitization phase may begin immediately or there may be a surrender period, during which you can’t access the funds without paying a penalty. There are annuities with minimum initial payments of $100,000 and some as low as $2,500. The more you deposit, typically, the larger your monthly payments will be.